Android Service
Service Lifecycle
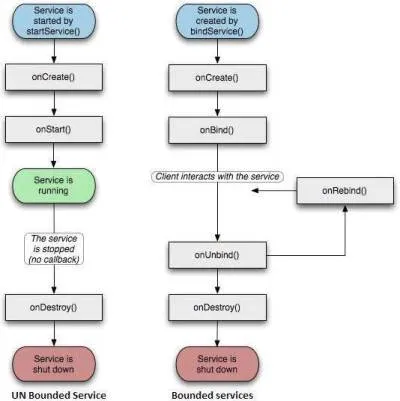
A Service has two states; Started and Bound.
- Started - A service is started when an application component, such as an activity, starts it by calling
startService(). Once started, a service can run in the background indefinitely, even if the component that started it is destroyed. - Bound - A service is bound when an application component binds to it by calling
bindService(). A bound service offers a client-server interface that allows components to interact with the service, send requests, get results, and even do so across processes with interprocess communication (IPC).
Callbacks
onStartCommand()- The system calls this method when another component, such as an activity, requests that the service be started, by callingstartService(). If you implement this method, it is your responsibility to stop the service when its work is done, by callingstopSelf()orstopService()methods.onBind()- The system calls this method when another component wants to bind with the service by callingbindService(). If you implement this method, you must provide an interface that clients use to communicate with the service, by returning anIBinderobject. You must always implement this method, but if you don’t want to allow binding, then you should return null.onUnbind()- The system calls this method when all clients have disconnected from a particular interface published by the service.onRebind()- The system calls this method when new clients have connected to the service, after it had previously been notified that all had disconnected in itsonUnbind(Intent).onCreate()- The system calls this method when the service is first created usingonStartCommand()oronBind(). This call is required to perform one-time set-up.onDestroy()- The system calls this method when the service is no longer used and is being destroyed. Your service should implement this to clean up any resources such as threads, registered listeners, receivers, etc.
